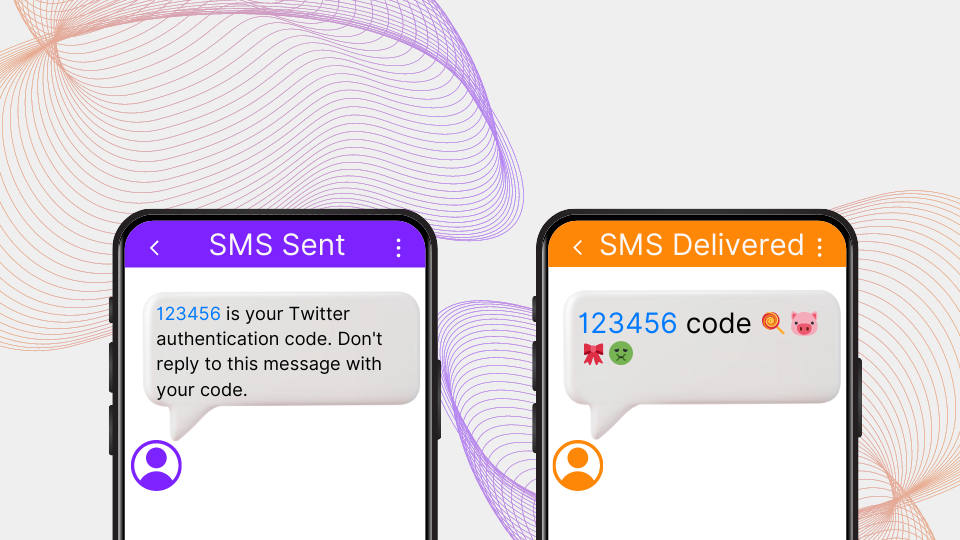
Navigating the world of SMS communication can seem straightforward until you consider the intricate details that make a significant difference. One such crucial aspect, often overlooked but pivotal to effective messaging, is the SMS Sender ID.
Ever wonder why some text messages immediately stand out, making you instantly recognize the sender, whether it’s your bank, a favorite online store, or your healthcare provider? That’s the power of a meticulously chosen SMS Sender ID.
Dive into this comprehensive guide to uncover the nuances of Sender IDs, their types, the intricacies of regulations, and the importance of ensuring your chosen ID resonates effectively with your audience.
What is Sender ID?
Sender ID is a unique identifier used in SMS messaging to indicate the originator of the message. In simpler terms, it’s the name or number that displays as the “sender” when someone receives an SMS on their phone. Think of it as the envelope’s return address, giving the recipient an immediate idea of who’s reaching out.
The Sender ID isn’t just arbitrarily chosen. Its establishment involves a series of steps and often requires the approval of network operators or regulatory bodies. Here’s how this process looks in general:
- Selection: Companies decide on a Sender ID, whether they prefer an alphanumeric representation of their brand or a specific number.
- Registration & Approval: Depending on the country or region, this chosen Sender ID might need registration. Some countries have strict regulations where only registered Sender IDs are allowed for A2P (Application-to-Person) messaging.
- Integration with SMS Aggregators: Once approved, the Sender ID is integrated into the SMS platform or aggregator being used. It becomes the default “from” address for all outgoing messages.
- Transmission: When an SMS is sent, the network uses this Sender ID to show the recipient the source of the message. Some networks and countries allow for dynamic Sender IDs (where it can be changed per message), while others might lock it to a fixed ID. In the process of transmission, the Sender ID might be modified or completely changed due to a number of reasons.
- Reception: On the recipient’s end, their mobile device reads the Sender ID information and displays it.
To wrap it up, the Sender ID serves as a pivotal touchpoint in SMS communications, bridging the gap between sender and recipient and ensuring that the message’s origin is transparent and recognizable.
Types of Sender ID
Each type of Sender ID has its own characteristics, advantages, and use cases. Let’s explore these types and learn which one might best align with your needs.
Alphanumeric Sender ID
Description: A combination of letters and numbers, this Sender ID type typically spans up to 11 characters. Often, it resonates with a brand’s name, motto, or campaign slogan, ensuring instant recognition.
Example: “AirlineSupport,” “Deal4U,” “Bank1Alert.”
Allowed length and characters: Up to 11 characters long. Can include upper- and lower-case ASCII letters. Can include spaces.
Best For: Brands aiming for immediate recognition and businesses wanting to maintain a consistent identity across various marketing channels.

Numeric Sender ID
Long Number (MSISDN):
Description: These mirror traditional phone numbers, offering a more direct and personal touch, as if the message is coming from another individual’s phone.
Example: “+14155552671”Allowed length: 15 digits and additionally a “+”
Best For: Businesses that prefer a localized touch, or in instances where a personal touch in communications is essential, such as appointment reminders or customer service follow-ups.
Shortcodes:
Description: Concise, typically 5 or 6 digits long, shortcodes are optimal for campaigns, contests, or other mass communication where ease of recognition and memorability are key. A two-way messaging is usually possible with the shortcodes.
Example: “12302” or “56789.”
Best For: Marketing campaigns, voting systems, customer feedback channels, and other scenarios where quick interactions are anticipated.
Shared Shortcodes
Description: These are the shortcodes that are shared by multiple companies. In this case, the two-way messaging is possible by using keywords in the reply.
Example: same as shortcodes in general
Best for: Small businesses, solo-entrepreneurs.
How to Select the Ideal Sender ID for Your Business
- For building brand image – alphanumeric. If building a robust and immediately recognizable brand image is paramount, opt for an Alphanumeric Sender ID. It ensures consistency and immediate brand recognition.
- For passing sensible Information – alphanumeric. If your company sends sensitive data over SMS (for example, OTP codes) it also makes sense to choose a custom Alphanumeric Sender ID to create a sense of security for a client.
- For lesser costs – shared shortcodes. If you’re a budding business or trying to minimize expenses, a shared number might be the way to go. However, ensure your messages are clear to avoid potential confusion.
- For interaction – shortcodes. If you anticipate two-way communications, like feedback or voting, shortcodes are excellent. Their brevity makes them easy for users to remember and engage with.
- For more personalization – long numeric. For infrequent and highly personalized communications, like appointment reminders or service notifications, Long Numeric IDs might be apt.
Aligning your business goals with the advantages of each Sender ID type will illuminate the path best suited for you. It’s not just about sending a message; it’s about establishing identity, trust, and rapport. However, the choice of Sender ID type doesn’t depend solely on your business needs. Numerous regulations need to be taken into consideration.
Rules and Regulations Surrounding Sender ID
Sender ID carries with it responsibilities and regulations, weaving a complex web of do’s and don’ts across different geographies and carriers.
But why do these restrictions exist in the first place? There are several reasons for this:
- To protect consumers from malicious practices like smishing (SMS phishing) and ensure that they can trust the messages they receive.
- To ensure that businesses don’t impersonate others, maintaining a clear line of communication and trust between a brand and its consumers.
- To prevent network congestion, potential abuses, or malpractices which might degrade the quality of the network.
Regulations to Consider
Country-level Regulations
In certain countries, A2P (Application-to-Person) messaging is permissible only when Sender IDs are registered with network operators. This whitelisting process ensures only legitimate businesses send messages.
Additionally, some regions dictate that the sender’s information must be integrated within the message body, ensuring recipients have clarity about the message’s origin.
Another restriction is that certain Sender ID types maybe forbidden in certain countries.
So when you are planning out sending SMS internationally, check out regulations in countries from your roadmap with your provider.
Mobile Operators
Considering the global dynamics of SMS, various mobile network operators have distinct measures to regulate messaging:
- Restrictions on Sender Types: Many carriers restrict or disallow certain types of Sender IDs. For instance, a few might not support alphanumeric IDs, while others might insist on it.
- Content Guidelines: Some operators have guidelines about the content of messages, especially if they seem promotional or have links embedded.
Spam Filters & Firewalls
Mobile operators and third-party services deploy filters to catch spam or potential threats. These filters, while essential for safety, sometimes inadvertently block genuine messages. Adhering to Sender ID rules and ensuring transparent content can help bypass these filters.
Ensuring Your Signature Arrives Intact: How to Test Your Sender ID
You’ve put meticulous thought into crafting the ideal Sender ID—one that mirrors your business ethos and obeys the labyrinth of regulations. Still, the journey between hitting “send” and your message landing in the recipient’s inbox is fraught with uncertainties. How can you make sure your Sender ID Arrives at its destination without changes? Here’s your roadmap.
The DIY Method and Its Flaws:
You could go old-school and send test messages to yourself, your team, and even your family and friends. But let’s be real: it’s like trying to predict a hurricane’s path by watching a butterfly. Chances are, this hit-or-miss method won’t emulate the actual networks your campaign will traverse.
The Professional Pathway with TelQ:
In a complex landscape, you want your Sender ID testing to be as close to the real-world scenario as possible. That’s why opting for a specialized SMS testing tool like TelQ isn’t just smart—it’s crucial. Here’s how to ensure that your Sender ID makes it through the SMS maze with its integrity intact.
- Mimic Your Desired Sender ID
Type in a Sender ID that reflects what you intend to use in your live campaign. The more accurate you are here, the better your test results will be.
- Mimic Your Desired Sender ID
- Utilize Ready-Made Templates
For added convenience, select from an array of pre-configured Sender IDs. This streamlines the process and ensures that you’re testing against standardized IDs that have a history of effective use.
- Utilize Ready-Made Templates
- Craft Your Test Message
Write a message that mimics the content of your planned live send-out. Incorporate TelQ’s dynamic ID; this special identifier enables the platform to track the sent message and extract insightful data from the receiving end. Pro tip: use available templates to fast-track this process.
- Craft Your Test Message
- Pick Network to Test
Choose the country and network you’re aiming to reach. Your test SMS will be dispatched to an actual number operating in this geography and network, rendering your test results substantially more reliable.
- Pick Network to Test
- Break Down the Results
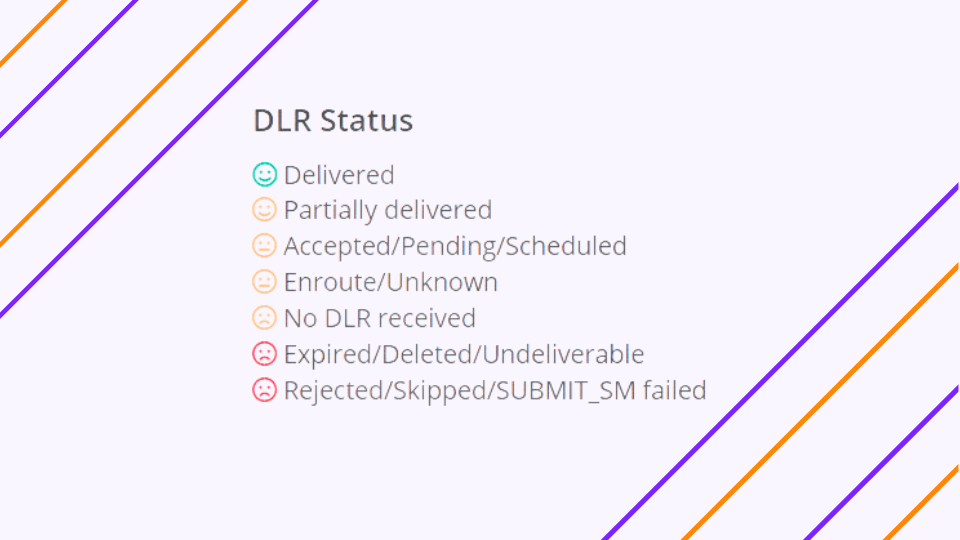
After you’ve conducted the test, you’ll gain valuable insights like:- The actual delivery status vs. the status reported by the supplier. This can help you sniff out any fake delivery reports.

- The actual delivery status vs. the status reported by the supplier. This can help you sniff out any fake delivery reports.
- Whether your Sender ID arrived as sent or was switched out en route.

- Whether your Sender ID arrived as sent or was switched out en route.
- If your message content remained untouched or underwent some form of alteration.

- If your message content remained untouched or underwent some form of alteration.
- Additional info such as SMSC data and more.

By sticking to this rigorous testing regimen, you can verify the robustness of your Sender ID, reducing surprises when you launch your full-scale campaign. Trust us, a little caution today can save a heap of regret tomorrow.
In conclusion
Whether you’re a burgeoning start-up or a seasoned enterprise, the right Sender ID can significantly bolster brand recognition, foster trust, and enhance the user experience. From the nuanced regulations to the varied types that best suit your business goals, it’s clear that this humble identifier serves as a pivotal bridge between you and your audience.
In a digital world awash with information, standing out is more crucial than ever. Choosing the right Sender ID isn’t just about transmitting a message; it’s about establishing an impactful presence in your customer’s world. So, the next time you send out an SMS campaign, remember: the devil is in the details, and those details could make all the difference.
Found this guide useful? Have more questions about SMS Sender IDs? Feel free to leave a comment below or reach out to us. We’re here to help you make the most of your SMS marketing campaigns.